1 福建医科大学附属福州市第一医院福州 350000
2 福建省妇幼保健院福州 350005
3 中山大学附属第三医院广州 510630
乳腺癌放疗误差主要由摆位误差和呼吸运动组成,通过准确测量摆位误差为乳腺癌计划靶区体积(PTV)外扩范围提供临床参考依据,提高治疗精度。测量2021年6月至10月采用发泡胶固定的31例乳腺癌患者的摆位误差。每一例患者在治疗前三次以及治疗后的每周进行一次锥形束CT(CBCT)扫描,将获取的CBCT图像与治疗计划CT进行骨性配准,并记录配准结果得到摆位误差值,分析摆位误差,并据此计算PTV外放边界的大小。结果显示:31例患者共行131次CBCT扫描,X(左右)、Y(头脚)和Z(腹背)方向的系统误差和随机误差的标准差分别是1.40 mm和0.67 mm、1.89 mm和0.56 mm、1.68 mm和1.16 mm;摆位误差的绝对值最大分别为4.9 mm、6.4 mm、8.7 mm;5.0 mm内误差在X、Y、Z方向分别占100%、98.47%、93.89%;X、Y、Z方向摆位误差小于3 mm的发生率分别为88.55%、79.39%、75.57%。经公式计算,得到本科室治疗乳腺癌临床靶区体积(CTV)到PTV外扩理论边界三个方向分别为3.98 mm、5.11 mm、5.02 mm。结果提示:发泡胶固定的乳腺癌调强放疗中,基于经验PTV外放边界的大小不能准确反映实际的摆位误差,需要基于CBCT测量和分析摆位误差、计算PTV外扩边界、指导临床靶区勾画范围具有实际的临床意义。
乳腺癌 发泡胶 调强放射治疗 摆位误差 外扩边界 Breast cancer Styrofoam Intensity modulated radiotherapy Setup error Extended boundary 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报
2022, 40(5): 050302
1 吉林大学原子与分子物理研究所,吉林 长春 130012
2 吉林大学吉林省应用原子分子光谱重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012
利用改进的马赫-曾德尔干涉仪测量了拉盖尔-高斯(LG)光束的轨道角动量(OAM)[拓扑电荷(TC)的值和符号]。模拟结果与实验结果一致。当LG光束与高斯光束发生干涉时,可以观察到类似漩涡的“花瓣”图案。“花瓣”的数量等于LG光束的TC的绝对值,干涉图样的旋转方向与TC符号有关:在TC符号为正时,干涉图样显示顺时针旋转;而在TC符号为负时,干涉图样显示逆时针旋转。只有当LG光束的光斑尺寸小于高斯光束的光斑尺寸时,才能根据干涉图样准确确定OAM状态。当LG光束的光斑尺寸接近高斯光束时,干涉图样只反映TC值,无法识别TC的符号。与传统干涉仪相比,该干涉仪可以获得稳定的干涉图样,并直接获得LG光束的OAM状态。实验现象是明显的。该研究结果为LG光束与高斯光束干涉的理论分析提供了参考,为光与物质之间的自旋-轨道相互作用奠定了研究基础。
衍射与光栅 涡旋光束 轨道角动量 马赫-曾德尔干涉仪 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(17): 1705001
1 吉林化工学院理学院, 吉林 吉林 132022
2 吉林大学原子与分子物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130012
3 吉林大学吉林省应用原子分子光谱重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130012
在大气环境中,研究平行板约束对激光诱导PMMA等离子体中CN分子光谱的影响,测量得到的5条光谱峰所处波长分别为388.29 nm(0-0)、387.0 nm(1-1)、386.14 nm(2-2)、385.44 nm(3-3)及385.03 nm(4-4)。实验结果表明,空间约束下的CN分子光谱峰强度明显高于无空间约束下的。另外,通过拟合CN光谱获得了CN分子的振动温度,结果显示,空间约束下的CN分子的振动温度明显高于无空间约束下的振动温度,且高激光能量下的CN分子振动温度高于低激光能量下的振动温度。平行板反射冲击波压缩等离子体羽,使得其温度和数密度增加,增强了激光诱导PMMA等离子体中CN分子的光谱强度。
光谱学 激光诱导击穿光谱 空间约束 光谱增强 振动温度
1 吉林化工学院理学院, 吉林 吉林 132022
2 吉林大学原子与分子物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130012
3 吉林省应用原子分子光谱重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130012
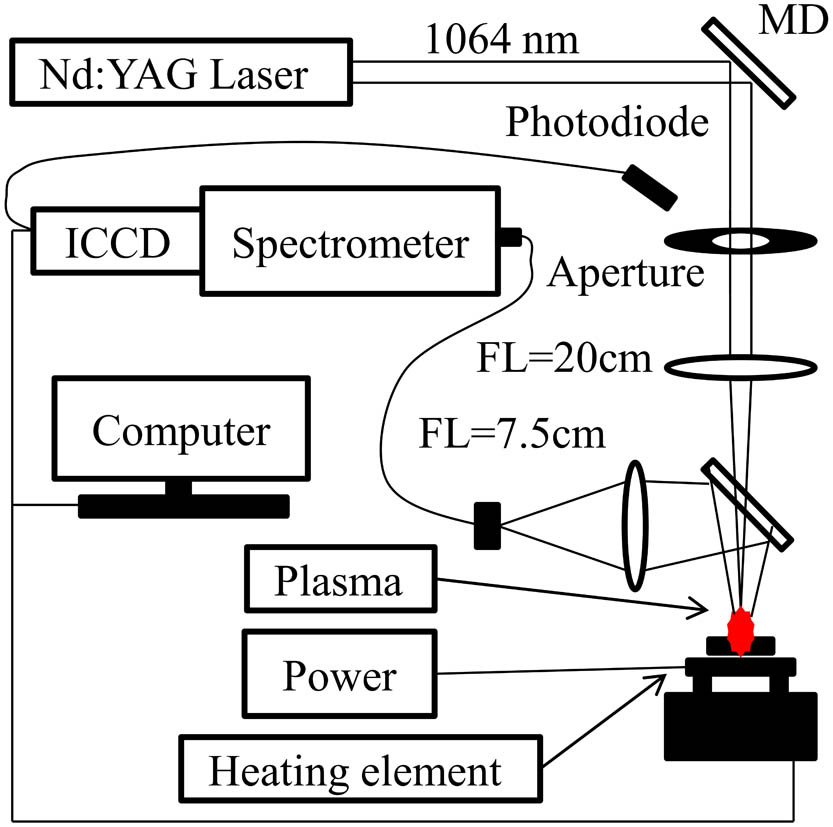
利用Nd∶YAG纳秒激光脉冲烧蚀硅产生等离子体光谱,通过改变聚焦透镜到样品表面的距离,研究硅等离子体光谱中原子谱线强度和离子谱线强度的变化,主要讨论的谱线为Si(I) 390.55 nm和Si(II) 385.60 nm。结果表明:Si(I)谱线强度和Si(II)谱线强度的变化依赖于透镜到样品表面的距离,随着透镜到样品表面的距离的增大,谱线强度先升高后降低;当样品表面远离焦点时,Si(I)谱线强度高于Si(II)谱线强度;当样品表面接近焦点时,Si(II)谱线强度高于Si(I)谱线强度;激光能量密度升高可使产生的等离子体中更多的原子电离成离子,使得离子谱线强度升高;改变透镜到样品表面的距离能优化激光诱导击穿光谱的辐射强度,同时能优化离子谱线强度与原子谱线强度的比值。
光谱学 激光诱导击穿光谱 透镜到样品表面的距离 原子谱线 离子谱线 硅 中国激光
2019, 46(11): 1111001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy (Jilin University), Changchun 130012, China
3 Aviation University of Air Force, Changchun 130021, China
We investigate the temperature dependence of the emission spectrum of a laser-induced semiconductor (Ge and Si) plasma. The change in spectral intensity with the sample temperature indicates the change of the laser ablation mass. The reflectivity of the target surface is reduced as the sample is heated, which leads to an increase in the laser energy coupled to the surface of the sample and eventually produces a higher spectral intensity. The spectral intensities are enhanced by a few times at high temperatures compared with the cases at low temperatures. The spectral intensity of Ge is enhanced by 1.5 times at 422.66 nm, and 3 times at 589.33 nm when the sample temperature increases from 50°C to 300°C. We can obtain the same emission intensity by a more powerful laser or by less pulse energy with a higher sample temperature. Based on experimental observations we conclude that the preheated sample can improve the emission intensity of laser-induced semiconductor plasma spectroscopy.
300.6365 Spectroscopy, laser induced breakdown 350.5400 Plasmas Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 123001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy (Jilin University), Changchun 130012, China
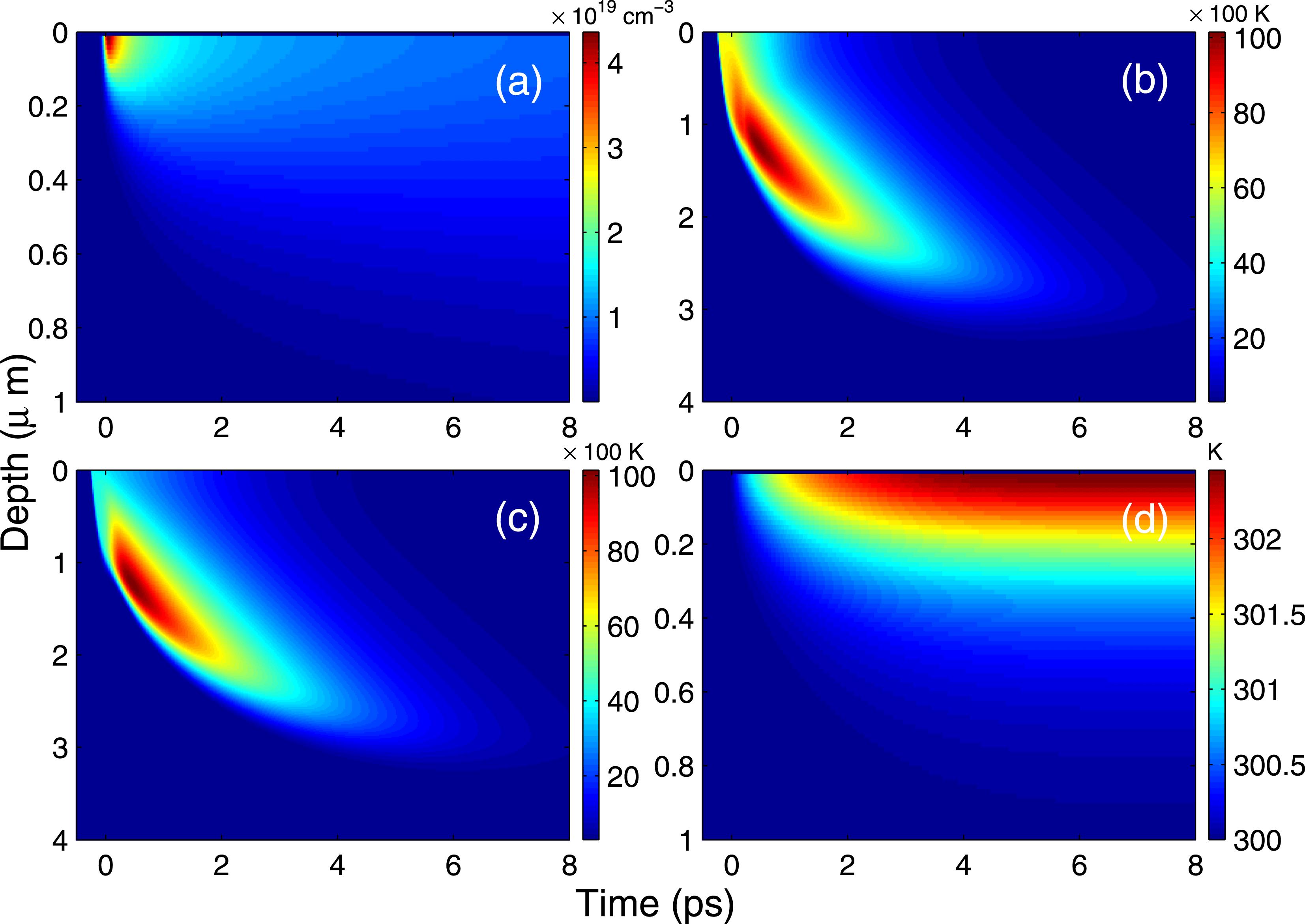
The ultrafast dynamic process in semiconductor Ge irradiated by the femtosecond laser pulses is numerically simulated on the basis of van Driel system. It is found that with the increase of depth, the carrier density and lattice temperature decrease, while the carrier temperature first increases and then drops. The laser fluence has a great influence on the ultrafast dynamical process in Ge. As the laser fluence remains a constant value, though the overall evolution of the carrier density and lattice temperature is almost independent of pulse duration and laser intensity, increasing the laser intensity will be more effective than increasing the pulse duration in the generation of carriers. Irradiating the Ge sample by the femtosecond double pulses, the ultrafast dynamical process of semiconductor can be affected by the temporalinterval between the double pulses.11474129), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education in China (grant no. 20130061110021) and the Project 2015091 Supported by Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University.
carrier carrier energy transfer energy transfer femtosecond laser femtosecond laser lattice lattice semiconductor semiconductor High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2016, 4(2): 02000e12

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy (Jilin University), Changchun 130012, China
Our experiments show that external focusing and initial laser energy strongly influences filament generated by the femtosecond Ti–sapphire laser in air. The experimental measurements show the filament length can be extended both by increasing the laser energy and focal length of focusing lens. On the other hand, the plasma fluorescence emission can be enhanced by increasing the laser energy with fixed focal length or decreasing the focal length. In addition, the collapse distance measured experimentally are larger than the calculated ones owing to the group-velocity-dispersion effect. In addition, we find that the line widths of the spectral lines from N2 is independent of filament positions, laser energies and external focusing.11504129), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20130061110021), and the Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (No. 2015091).
femtosecond laser femtosecond laser filament filament fluorescence fluorescence High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2016, 4(1): 010000e7
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy (Jilin University), Changchun 130012 , China
The influence of group velocity dispersion (GVD) on the self-focusing of femtosecond laser pulses is investigated by numerically solving the extended nonlinear Schr?dinger equation. By introducing the GVD length LGVD into the semi-empirical, self-focusing formula proposed by Marburger, a revised one is proposed, which can not only well explain the influence of GVD on the collapse distance, but also is in good agreement with the numerical results, making the self-focusing formula applicable for more cases.
190.5530 Pulse propagation and temporal solitons 190.0190 Nonlinear optics 190.3270 Kerr effect 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 121901





